| |
RAID Level: |
0 |
[ 1 ] |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
10 |
53 |
0+1 |
next |
|
|
|
RAID 1: Mirroring and Duplexing 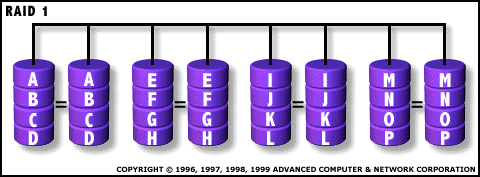
For Highest performance, the controller must be able to perform two concurrent separate Reads per mirrored pair or two duplicate Writes per mirrored pair.
RAID Level 1 requires a minimum of 2 drives to implement |
|
|
|
Characteristics/Advantages
One Write or two Reads possible per mirrored pair
Twice the Read transaction rate of single disks, same Write transaction rate as single disks
100% redundancy of data means no rebuild is necessary in case of a disk failure, just a copy to the replacement disk
Transfer rate per block is equal to that of a single disk
Under certain circumstances, RAID 1 can sustain multiple simultaneous drive failures
Simplest RAID storage subsystem design |
|
|
|
Disadvantages
Highest disk overhead of all RAID types (100%) - inefficient
Typically the RAID function is done by system software, loading the CPU/Server and possibly degrading throughput at high activity levels. Hardware implementation is strongly recommended
May not support hot swap of failed disk when implemented in "software" |
|
|
|
Copyright © 2000, 2001 Advanced Computer & Network Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |