| |
RAID Level: |
0 |
1 |
[ 2 ] |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
10 |
53 |
0+1 |
next |
|
|
|
RAID 2: Hamming Code ECC 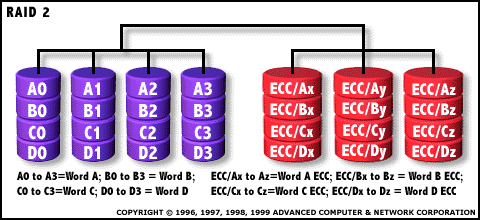
Each bit of data word is written to a data disk drive (4 in this example: 0 to 3). Each data word has its Hamming Code ECC word recorded on the ECC disks. On Read, the ECC code verifies correct data or corrects single disk errors. |
|
|
|
Characteristics/Advantages
"On the fly" data error correction
Extremely high data transfer rates possible
The higher the data transfer rate required, the better the ratio of data disks to ECC disks
Relatively simple controller design compared to RAID levels 3,4 & 5 |
|
|
|
Disadvantages
Very high ratio of ECC disks to data disks with smaller word sizes - inefficient
Entry level cost very high - requires very high transfer rate requirement to justify
Transaction rate is equal to that of a single disk at best (with spindle synchronization)
No commercial implementations exist / not commercially viable |
|
|
|
Copyright © 2000, 2001 Advanced Computer & Network Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |