| |
RAID Level: |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
10 |
53 |
[ 0+1 ] |
|
|
|
RAID 0+1: High Data Transfer Performance 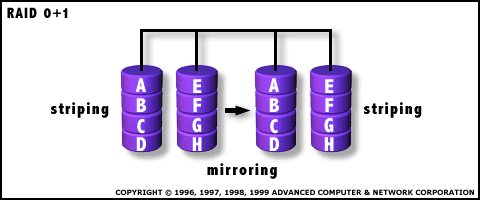
RAID Level 0+1 requires a minimum of 4 drives to implement |
|
|
|
Characteristics/Advantages
RAID 0+1 is implemented as a mirrored array whose segments are RAID 0 arrays
RAID 0+1 has the same fault tolerance as RAID level 5
RAID 0+1 has the same overhead for fault-tolerance as mirroring alone
High I/O rates are achieved thanks to multiple stripe segments
Excellent solution for sites that need high performance but are not concerned with achieving maximum reliability |
|
|
|
Disadvantages
RAID 0+1 is NOT to be confused with RAID 10. A single drive failure will cause the whole array to become, in essence, a RAID Level 0 array
Very expensive / High overhead
All drives must move in parallel to proper track lowering sustained performance
Very limited scalability at a very high inherent cost |
|
|
|
Copyright © 2000, 2001 Advanced Computer & Network Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |